
February 12th, 2024
Restaurant payment processing encompasses both front-end and back-end processes, from the moment a customer places an order to the completion of payment. Efficient payment processing is paramount for restaurants as it directly impacts customer satisfaction, operational efficiency, and financial performance.
In an industry where speed and convenience are key, seamless payment transactions contribute to a positive dining experience, encourage repeat business and enhance the restaurant’s reputation while reducing the risk of errors. Implementing robust payment processing systems and strategies is essential for ensuring the smooth operation and success of any restaurant.
Most restaurants partner with payment processing providers which handle all payments for a restaurant and integrate online orders, in-store orders and provide multiple payment options. Deciding which payment processing provider is an important decision for any restaurant and in this article will take a look at key consideration factors.
Payment processing fees for a restaurant typically involve several components, which can vary depending on the payment processing provider and the terms of your agreement. Listed below are the types of fees your restaurant will pay when using payment processing provider.
Transaction Fees: These fees are charged for each transaction processed through your payment system. They can be a flat rate or a percentage of the transaction amount, or sometimes a combination of both. For example, you might pay $0.10 per transaction plus 0.5% of the transaction amount.
Interchange Fees: Interchange fees are charged by the credit card networks (such as Visa, Mastercard, or American Express) and are typically the largest portion of your processing costs. These fees are paid to the card-issuing banks and are set by the networks based on various factors such as the type of card used, the transaction method (e.g., swiped, dipped, or keyed-in), and the risk associated with the transaction.
Assessment Fees: Assessment fees are charged by the credit card networks and are typically a small percentage of the transaction amount. These fees are separate from interchange fees and are paid directly to the networks.
Monthly Fees: Some payment processors may charge monthly fees for access to their services or for additional features such as reporting tools or customer support.
Statement Fees: These fees cover the cost of providing you with monthly statements detailing your transaction activity. They are usually charged on a per-statement basis.
Gateway Fees: If you accept payments online or through a virtual terminal, you may incur gateway fees. These fees cover the cost of connecting your payment system to the credit card networks.
Chargeback Fees: Chargeback fees are incurred when a customer disputes a transaction and requests a refund from their credit card issuer. These fees can vary depending on the processor and are typically passed on to the merchant along with the disputed amount.
One of the key things to keep in mind when debating between different payment processing providers is that the quoted fee per transaction is only a part of the total fees your restaurant will pay per transaction.
To illustrate this, let’s look at the comparison example of two providers that quote you different rates and see how much your restaurant will pay in total fees on monthly sales of $50,000.
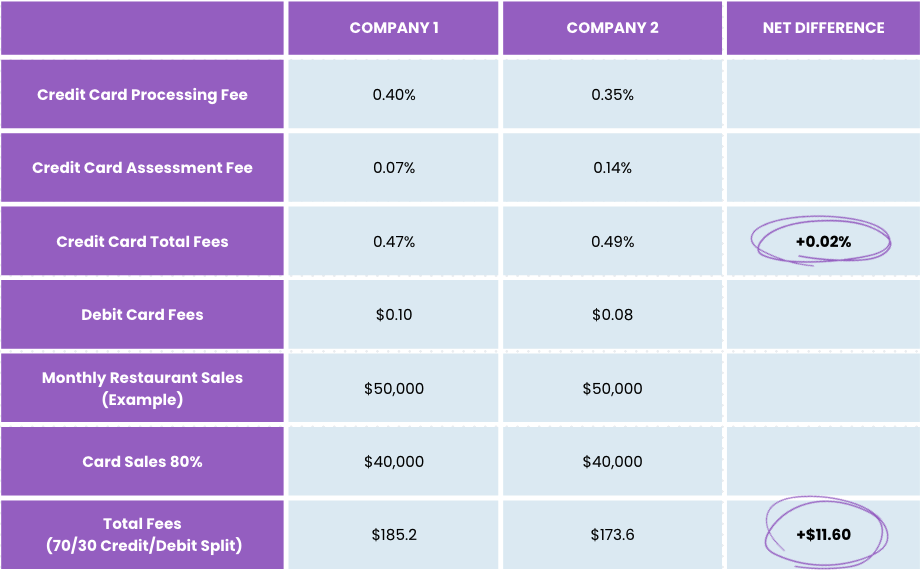
Despite having higher quoted credit card processing fee by 0.05%, company one will only charge $11.60 more in fees than company two on monthly sales of $50,000.
This is why it’s important to understand total fee structure when it comes to payment processing and not just base it on initial quoted credit card fee rate.
Integrations play a crucial role in streamlining operations and enhancing the efficiency of restaurant payment processing. It’s also important to consider possible integrations to ensure longevity of payment processing and adaptability to emerging trends in the restaurant industry. Here are some key integrations you must consider when picking a restaurant payment processor:
Point-of-Sale (POS) Systems: Integration with a POS system is essential for seamless payment processing. It allows transactions to be processed directly within the POS interface, eliminating the need for manual entry and reducing the risk of errors.
Online Ordering Platforms: If your restaurant offers online ordering for pickup or delivery, integration with online ordering platforms is essential. This integration enables customers to place orders online and pay securely through your website or mobile app.
Mobile Payment Solutions: Integrating with mobile payment solutions such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, and Samsung Pay allows customers to make payments using their mobile devices. This provides added convenience and flexibility for customers while reducing transaction times and enhancing security.
Gift Card and Loyalty Programs: Integrating with gift card and loyalty program providers allows you to offer and manage gift cards and loyalty rewards directly through your payment processing system. This encourages repeat business, increases customer loyalty, and provides valuable insights into customer behavior and spending patterns.
Fraud Detection and Prevention Tools: Integrating with fraud detection and prevention tools helps protect your restaurant from fraudulent transactions and chargebacks. These tools use advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques to analyze transaction data in real-time and identify suspicious activity.
By leveraging these integrations, restaurants can streamline payment processing, enhance the customer experience, and gain valuable insights into their operations to drive growth by recognizing that a transaction is more than just a payment.
Ease of use is essential for restaurant payment processing systems to ensure smooth and efficient operations for both, the restaurant and its customers. Here are the top five ease of use features you need to consider.
Intuitive User Interface: Clear and intuitive design elements, such as large buttons, simple menu structures, and visual cues, can help streamline the transaction process and reduce the likelihood of errors.
Quick Transaction Processing: Speed is critical and includes minimizing the time it takes to complete each transaction, whether it’s swiping a card, entering a PIN, or processing a contactless payment. Any delays in processing payments can lead to longer wait times for customers and impact overall efficiency.
Offline Mode: In the event of an internet outage or technical issues, the payment processing system should have an offline mode that allows transactions to be processed offline and synced with the central server once connectivity is restored.
Customizable Settings and Preferences: Ability to set default tipping options, customize receipt formats, and adjust security settings can help optimize the user experience and ensure that the payment processing system aligns with the restaurant’s unique requirements.
Support for Multiple Payment Methods: The payment processing system should support a wide range of payment methods, including credit cards, debit cards, mobile payments, and cash. Also, support for split payments and tipping functionality can further enhance the flexibility and ease of use for both customers and staff.
When it comes to restaurant payment processing, offering a variety of payment methods can enhance customer convenience, satisfaction and even average order value. Listed below are some payment methods that your restaurant’s payment processor should offer to customers.
Credit and Debit Cards: Accepting credit and debit cards is essential for modern restaurants. Customers expect to be able to pay with their cards, whether it’s a traditional magnetic stripe card or an EMV chip card.
Mobile Payments: Mobile payment options such as Apple Pay, Google Pay, Samsung Pay, and other NFC-based payment methods are becoming increasingly popular. These solutions allow customers to make secure payments using their smartphones or other mobile devices, often with just a tap or a scan.
Online Payments: If your restaurant offers online ordering or delivery services, accepting online payments is essential. Customers should be able to securely pay for their orders through your website or mobile app using credit/debit cards, digital wallets, or other online payment methods.
Gift Cards and Vouchers: Offering gift cards and vouchers can boost sales and customer loyalty. Allow customers to purchase and redeem gift cards or vouchers for meals, drinks, or special promotions.
Split Payments and Tipping: Providing flexibility for split payments (where a single bill is divided among multiple customers) and tipping options is important for accommodating different dining scenarios.
Ensuring compliance and security in restaurant payment processing is crucial to protect both your customers’ sensitive information and your restaurant’s reputation. Here are some important compliance and security measures to consider:
PCI DSS Compliance: Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) compliance is a set of security standards designed to ensure that businesses that process, store, or transmit credit card information maintain a secure environment. Compliance with PCI DSS involves implementing security measures such as encryption, network segmentation, access controls, and regular security testing to protect cardholder data from unauthorized access or theft.
EMV Chip Card Acceptance: EMV (Europay, Mastercard, and Visa) chip cards are equipped with a microchip that generates a unique code for each transaction, making it more difficult for fraudsters to counterfeit cards or steal card information. Restaurants should use EMV-compliant payment terminals and encourage customers to use chip cards whenever possible to minimize the risk of card-present fraud.
Point-to-Point Encryption (P2PE): Point-to-Point Encryption (P2PE) is a security measure that encrypts cardholder data from the point of capture (e.g., payment terminal) until it reaches the payment processor’s secure environment. P2PE helps protect card data throughout the transaction process, reducing the risk of data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
Secure Network Infrastructure: Implement robust network security measures to protect payment data from unauthorized access or interception. This includes using firewalls, intrusion detection/prevention systems, strong encryption protocols, and secure Wi-Fi networks.
Employee Training and Awareness: Train your staff on best practices for handling payment transactions securely and recognizing potential security threats such as phishing scams or skimming devices. Emphasize the importance of following security protocols, verifying customer identities, and reporting any suspicious activity or incidents immediately.
Snappy offers a plug in play restaurant payment processing solution that checks off a lot of the things we discussed in this article. If you’re interested in getting a free demo of Snappy’s payment terminal, please fill out the form below.
A good credit card processing rate for a restaurant can vary between 0.25% and 0.5% depending on the features, integrations and fee structure that come with the payment processor.
Payment technology for restaurants encompasses a range of solutions designed to facilitate transactions and streamline the payment process for both customers and businesses
Payment processing typically involves several steps: Authorization, authentication, clearing, settlement and Reconciliation Each step must be completed accurately and securely to ensure successful payment processing.
Whether you can pass credit card fees along to customers depends on the laws and regulations in your jurisdiction, as well as the policies of the card networks (such as Visa, Mastercard, etc.) and your merchant agreement with your payment processor.